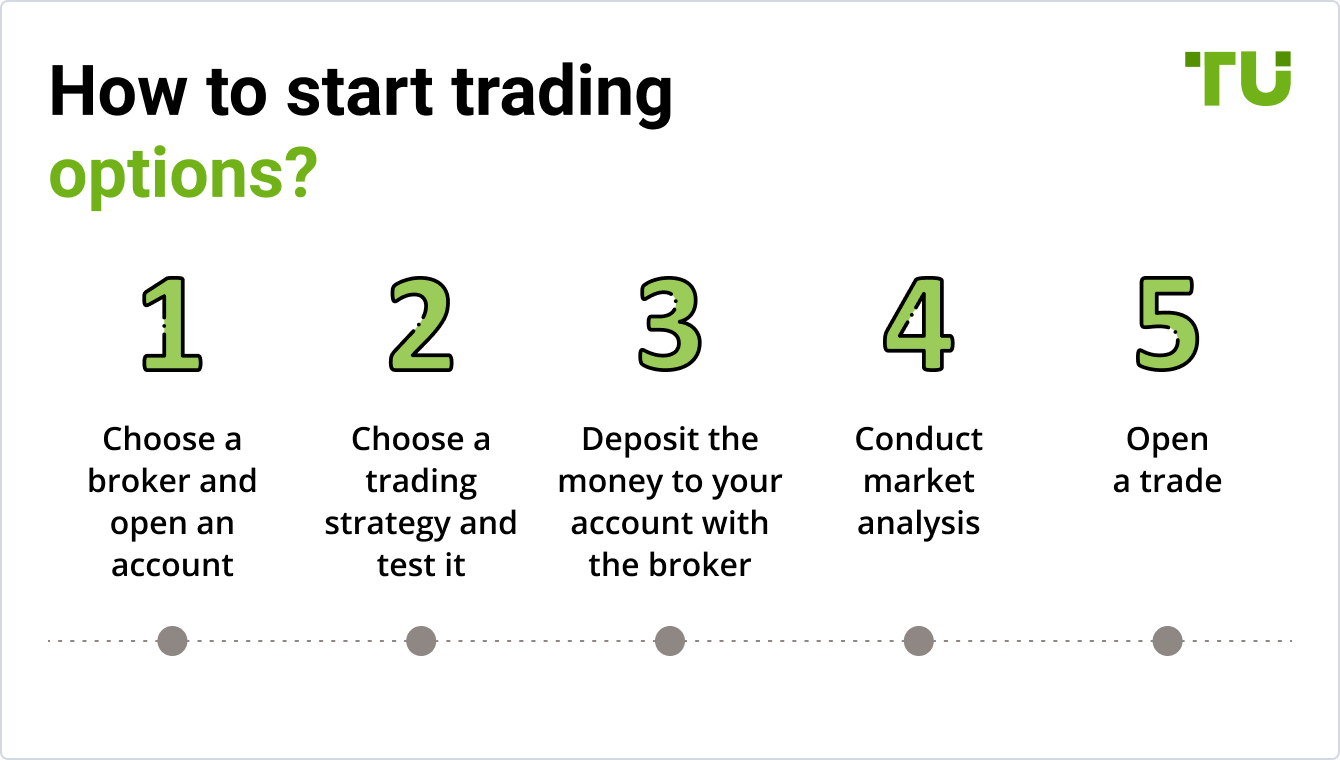
To trade options, open a brokerage account and learn the basics of options trading. Execute trades by buying or selling options contracts.
Options trading offers a flexible strategy to investors aiming to diversify their portfolios. It involves buying and selling contracts that grant the right, but not the obligation, to purchase or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price before a specific date.
This method requires understanding key concepts such as call and put options, strike prices, and expiration dates. Mastering these fundamentals can help traders make informed decisions and manage risks effectively. Engaging in options trading can enhance your investment approach and potentially yield significant returns if executed with a well-thought-out strategy.
Credit: tradersunion.com
Introduction To Options Trading
Options trading can seem complex at first. Yet, it offers many opportunities. This guide will help you understand the basics. Let’s start by learning what options are and their benefits.
What Are Options?
Options are contracts. They give the buyer the right to buy or sell an asset. This must happen at a specific price before a certain date. The asset could be stocks, bonds, or other securities.
There are two types of options:
- Call Options: These give the right to buy the asset.
- Put Options: These give the right to sell the asset.
Each option contract represents 100 shares of the underlying asset. Knowing the type of option is crucial for trading.
Benefits Of Trading Options
Trading options offers several benefits. Here are some key advantages:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Leverage | Control large positions with less capital. |
| Flexibility | Use various strategies to profit in different markets. |
| Hedging | Protect your investments from market risks. |
| Income Generation | Earn regular income through options strategies. |
These benefits make options trading attractive. It can be a powerful tool in your investment arsenal.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Types Of Options
Understanding the types of options is key to trading successfully. Options come in two main types: Call Options and Put Options. Each serves a different purpose and has unique characteristics. Let’s explore both in detail.
Call Options
A Call Option gives the buyer the right to purchase a stock. This purchase happens at a predetermined price, known as the strike price. The buyer can exercise this right until the option expires.
Here are some key points about Call Options:
- Buyer benefits if the stock price rises above the strike price.
- Seller benefits from the premium received for selling the option.
- Call options are often used for speculative purposes.
- Investors may also use them for hedging against potential losses.
Put Options
A Put Option gives the buyer the right to sell a stock. The sale happens at a predetermined price, known as the strike price. The buyer can exercise this right until the option expires.
Here are some key points about Put Options:
- Buyer benefits if the stock price falls below the strike price.
- Seller benefits from the premium received for selling the option.
- Put options are often used for speculative purposes.
- Investors may also use them for hedging against potential losses.
Options Trading Terminology
Understanding key terms is crucial in options trading. Let’s explore some essential terminology.
Strike Price
The strike price is the set price for an option. It’s the price at which the option can be exercised. For a call option, it’s where you can buy the asset. For a put option, it’s where you can sell the asset. The strike price affects the option’s value.
Expiration Date
The expiration date is the date when an option contract expires. After this date, the option becomes void. Traders must act before this date. The expiration date impacts the option’s price. Short-term options usually have higher volatility. Long-term options are less volatile.
Premium
The premium is the price paid for the option. It’s the cost to buy the option contract. The premium depends on various factors. These include the strike price, expiration date, and the asset’s volatility. Higher premiums mean more expensive options. Lower premiums mean cheaper options.
Below is a table summarizing these key terms:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Strike Price | The set price for exercising an option. |
| Expiration Date | The date when the option contract expires. |
| Premium | The cost to buy the option contract. |
Understanding these terms is vital. It helps in making informed trading decisions. Master these basics to excel in options trading.
Setting Up A Trading Account
Before you can start trading options, you need a trading account. This is the first step towards your trading journey. Let’s explore how you can set up your trading account.
Choosing A Broker
Choosing the right broker is essential for trading options. Look for a broker with a strong reputation. Ensure they offer low fees and commissions. Check if they provide a user-friendly platform.
Here’s a table that compares key features of some popular brokers:
| Broker | Fees | Platform Usability | Customer Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Broker A | Low | Very User-Friendly | 24/7 Support |
| Broker B | Medium | User-Friendly | 24/5 Support |
| Broker C | High | Moderate | Business Hours Support |
Account Requirements
Opening a trading account involves meeting certain requirements. Most brokers will need you to provide:
- Personal identification
- Proof of address
- Financial information
They may also ask about your trading experience. This helps them ensure you understand the risks.
Here’s an example of the steps you might follow:
- Choose your broker
- Fill out the application form
- Submit your identification documents
- Fund your account
Once your account is set up, you can start trading options. Make sure to review your broker’s platform and tools.
Basic Strategies For Beginners
Starting with options trading can be exciting. Beginners need simple strategies to understand the market. Three basic strategies are crucial: buying calls, buying puts, and covered calls.
Buying Calls
Buying calls is a popular strategy. It allows you to buy a stock at a set price. This is useful if you think the stock will go up.
- Pay a premium for the call option.
- Set a strike price, the price at which you can buy the stock.
- If the stock price rises above the strike price, you make a profit.
Buying calls can be profitable in a rising market. It requires less capital compared to buying the stock outright.
Buying Puts
Buying puts is another key strategy. This lets you sell a stock at a set price. Useful if you think the stock will fall.
- Pay a premium for the put option.
- Set a strike price, the price at which you can sell the stock.
- If the stock price falls below the strike price, you make a profit.
Buying puts can be profitable in a falling market. It provides a way to hedge against losses.
Covered Calls
Covered calls combine owning a stock with selling call options. This strategy can generate income from the stock you own.
- Own shares of the stock.
- Sell call options for those shares.
- Collect premiums from selling the call options.
Covered calls are less risky. They can provide a steady income stream.
| Strategy | Market Condition | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Buying Calls | Rising Market | High |
| Buying Puts | Falling Market | High |
| Covered Calls | Stable or Slightly Rising Market | Low |
Analyzing Market Conditions
Understanding how to trade options requires a keen eye on market conditions. Analyzing the market helps traders make informed decisions. This section will guide you through analyzing market conditions using technical and fundamental analysis.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying past market data. Traders use charts, patterns, and indicators to predict future movements. Here are some key tools:
- Charts: Line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts.
- Indicators: Moving averages, RSI, and MACD.
- Patterns: Head and shoulders, triangles, and flags.
Traders often rely on support and resistance levels. These levels help identify entry and exit points. Technical analysis focuses on price action and volume.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis examines a company’s financial health. It looks at earnings, revenue, and other financial metrics. Here are some important factors:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Earnings | Company’s net profit over a period. |
| Revenue | Total income from sales and services. |
| Debt | Company’s total liabilities. |
Fundamental analysis also considers economic indicators. These include GDP, inflation, and employment rates. This analysis helps determine a company’s intrinsic value.
Risk Management
Effective risk management is crucial in options trading. Without it, you might face significant losses. This section explains key strategies for managing risk.
Position Sizing
Position sizing is the amount of money you invest in a trade. Proper position sizing can help limit losses. It ensures you don’t risk too much on a single trade.
- Calculate your total trading capital.
- Decide the percentage you are willing to risk per trade.
- Adjust your position size based on this percentage.
For example, if you have $10,000 and choose to risk 2%, you should not risk more than $200 per trade.
Stop-loss Orders
A stop-loss order is a tool to limit your losses. It automatically sells your options when they reach a certain price.
- Determine your acceptable loss level.
- Set your stop-loss order at this price point.
This ensures you exit a trade before losses grow too large.
| Trading Capital | Risk Percentage | Maximum Risk per Trade |
|---|---|---|
| $10,000 | 2% | $200 |
| $20,000 | 1.5% | $300 |

Credit: www.amazon.com
Advanced Trading Strategies
Welcome to the advanced trading strategies section of options trading. Here, you’ll learn about Spreads, Straddles, and Strangles. These techniques can help manage risk and increase profits.
Spreads
A spread involves buying and selling options of the same class. This strategy can limit risk and reward. There are several types of spreads:
- Bull Call Spread: Buy a lower strike call and sell a higher strike call.
- Bear Put Spread: Buy a higher strike put and sell a lower strike put.
- Iron Condor: Sell a lower strike put and higher strike call while buying even lower strike put and higher strike call.
Spreads can help traders take advantage of specific market conditions.
Straddles
A straddle involves buying both a call and a put option. Both options have the same strike price and expiration date. This strategy profits from high volatility. It doesn’t matter which direction the market moves. It is useful when expecting significant price movement.
Strangles
A strangle is similar to a straddle but with different strike prices. Buy a call option and a put option. The call option has a higher strike price. The put option has a lower strike price. This strategy is cheaper than a straddle. It requires a significant move in the stock price to be profitable.
| Strategy | Components | Market Condition | Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bull Call Spread | Buy low call, sell high call | Rising market | Limited |
| Bear Put Spread | Buy high put, sell low put | Falling market | Limited |
| Iron Condor | Sell low put, sell high call, buy lower put, buy higher call | Stable market | Limited |
| Straddle | Buy call and put at same strike | High volatility | High |
| Strangle | Buy call and put at different strikes | High volatility | High |
Advanced trading strategies like spreads, straddles, and strangles offer diverse opportunities. They help traders navigate different market conditions.
Tools And Resources
Trading options can be overwhelming without the right tools and resources. These tools and resources help streamline the trading process. They also provide essential knowledge to make informed decisions.
Trading Platforms
Choosing the right trading platform is crucial for trading options. These platforms offer essential features and tools. They help you execute trades quickly and efficiently.
- Thinkorswim by TD Ameritrade: Known for its advanced charting tools.
- Interactive Brokers: Offers low commissions and diverse trading options.
- Robinhood: User-friendly and commission-free, suitable for beginners.
These platforms provide real-time data and analytics. This helps in making timely and informed trading decisions.
Educational Resources
A solid understanding of options trading is essential. Various educational resources can help you grasp the basics and advanced strategies.
- Online Courses: Websites like Coursera and Udemy offer comprehensive courses.
- Books: “Options as a Strategic Investment” by Lawrence McMillan is a must-read.
- Webinars: Many platforms offer free webinars hosted by experienced traders.
These resources cover a range of topics. They include risk management, trading strategies, and market analysis. This knowledge is vital for successful trading.
Here’s a quick comparison of some top educational resources:
| Resource | Type | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Coursera | Online Courses | Comprehensive Learning |
| Options as a Strategic Investment | Book | In-depth Knowledge |
| TD Ameritrade Webinars | Webinars | Real-Time Learning |
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Trading options can be profitable, but it has risks. Beginners often make mistakes. Learn to avoid these mistakes to succeed. This guide covers the most common errors traders make.
Overleveraging
Overleveraging occurs when traders use too much margin. This can lead to significant losses. Using high leverage might seem attractive. It can amplify gains but also increases risks. Many beginners get excited by potential profits and ignore the dangers. Always remember, higher leverage means higher risk.
To avoid overleveraging, start small. Use a lower percentage of your capital. This helps you manage risks better. For example, if you have $10,000, don’t risk more than $1,000 on a single trade. This way, even if you lose, you still have funds left to trade.
| Capital | Risk Per Trade |
|---|---|
| $10,000 | $1,000 |
| $5,000 | $500 |
Ignoring Risk Management
Ignoring risk management is a critical mistake. Many traders focus only on potential profits. They forget about potential losses. Good risk management strategies protect your capital. They help you stay in the game longer.
Here are some tips for effective risk management:
- Set stop-loss orders to limit losses.
- Do not put all your capital in one trade.
- Use position sizing to control risk.
For example, if trading options, you can set a stop-loss at 10%. This means if the trade goes against you, you only lose 10% of your investment. This strategy helps you avoid big losses and preserve your capital.
Remember, successful traders focus on risk management. They know that protecting their capital is key to long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
How To Do Option Trading Step By Step?
To start option trading, open a brokerage account. Learn basic terms and strategies. Analyze the market and select an option. Place your trade and monitor it. Close the trade to realize profit or loss.
How Do Beginners Trade Options Successfully?
Beginners can trade options successfully by educating themselves, starting small, using risk management, practicing with paper trading, and staying updated on market trends.
Can I Trade Options With $100?
Yes, you can trade options with $100. Focus on low-cost options and strategies. Start with proper research and risk management.
What Is The Trick For Option Trading?
Master risk management. Use stop-loss orders. Diversify your portfolio. Stay informed on market trends. Practice with paper trading.
Conclusion
Mastering options trading requires patience and practice. Follow this guide to build your confidence and skills. Remember, research and strategy are key. Stay informed and keep refining your approach. Happy trading!

Elaine C. Durham is a distinguished figure in the domain of new business investments, recognized for her expertise and strategic acumen in navigating the dynamic landscape of emerging ventures. With a robust educational background and a wealth of experience, Elaine has become a trusted authority in the field, contributing valuable insights to the realm of investment strategies for nascent businesses. Her professional journey is marked by a keen ability to identify promising opportunities, coupled with a shrewd understanding of market dynamics and risk management. Known for her innovative approach and successful endeavors, Elaine C. Durham stands as a beacon for entrepreneurs and investors alike, offering a wealth of knowledge on fostering growth and sustainability in the ever-evolving world of new business investments.