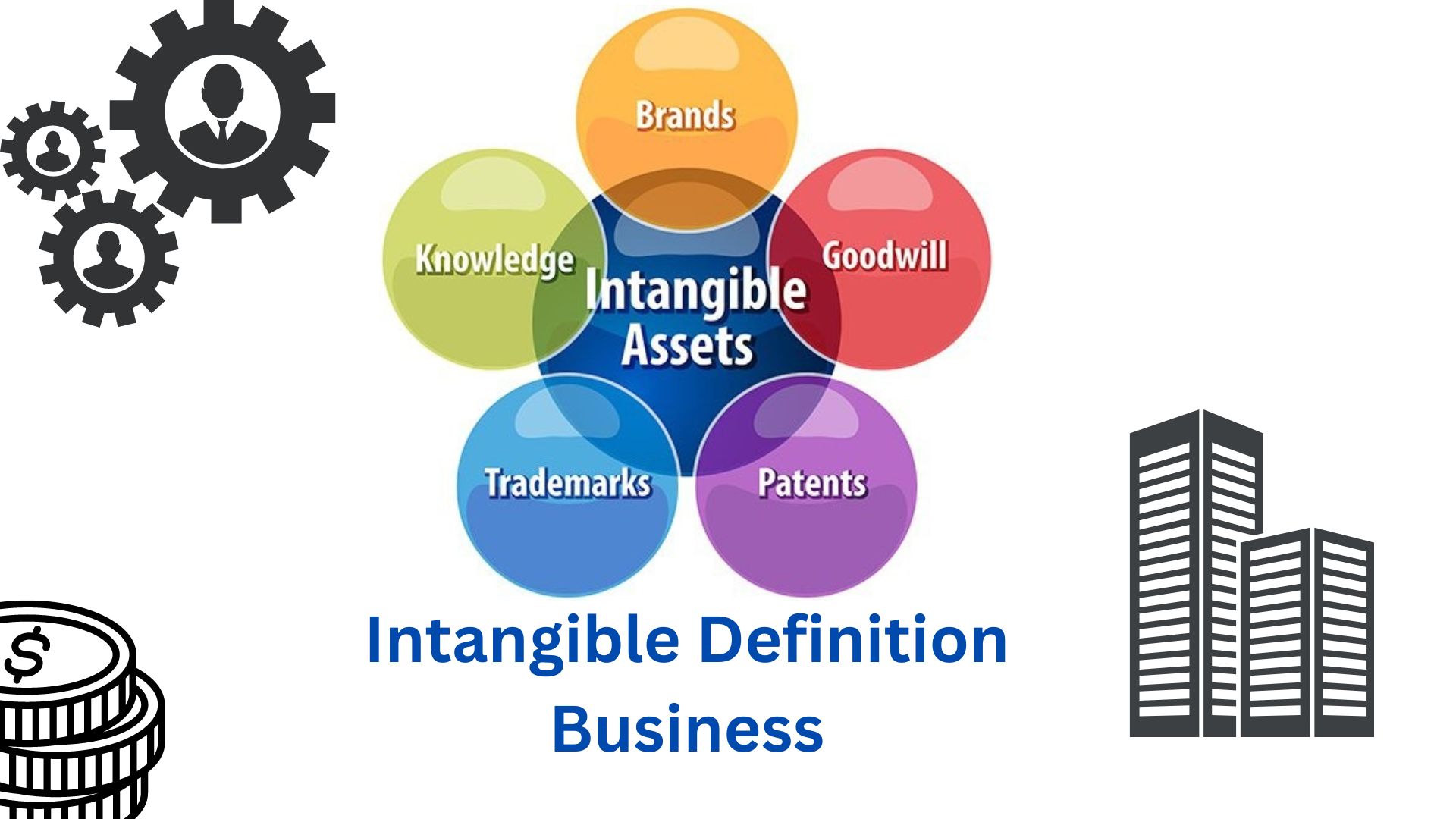
In business, intangible assets are non-physical assets that hold long-term value and are used by a company for more than one year. Examples of intangible assets include goodwill, brand recognition, copyrights, patents, trademarks, trade names, and customer lists.
These assets cannot be seen or touched but still contribute value to a business. Intangible assets are an important aspect of a company’s overall worth and can play a significant role in their success. Proper recognition and management of intangible assets are essential for businesses looking to maximize their value and competitive advantage.
What Are Intangibles?
Intangibles in business refer to assets that lack physical existence, such as goodwill, patents, trademarks, and customer lists. These assets hold long-term value and are vital for company operations and success. Intangible resources provide strategic information and assets that businesses can utilize to achieve their objectives.
Types Of Intangibles
Intangibles are assets that cannot be physically touched or seen, but they hold significant value for businesses. These intangible assets are vital for the success and growth of a company, as they provide a competitive advantage and contribute to its overall value. There are several types of intangibles that businesses can possess:
- Goodwill: Goodwill represents the reputation and positive relationship a company has built with its customers and stakeholders over time. It includes factors such as customer loyalty, brand recognition, and a strong brand image.
- Intellectual Property: Intellectual property includes patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. These assets protect a company’s innovations, inventions, and creative works from being copied or used by competitors without permission.
- Brand Equity: Brand equity refers to the value that a brand has in the minds of consumers. It is the result of consistent branding, quality products or services, and positive customer experiences.
- Customer Lists: A customer list is a database of existing and potential customers that a business has acquired or developed over time. It is a valuable asset as it allows companies to target their marketing efforts, personalize communication, and build customer relationships.
- Software and Technology: Software, applications, and technological infrastructure that are unique to a company can be considered intangible assets. These assets contribute to operational efficiency, process improvement, and competitive advantage.
Importance Of Intangibles In Business
Intangible assets play a crucial role in the success and sustainability of a business. They provide businesses with a competitive edge, differentiation, and added value in the market. Here are some reasons why intangibles are important:
- Competitive Advantage: Intangible assets such as brand reputation, customer loyalty, and intellectual property give businesses a competitive advantage over their rivals. These assets create barriers to entry, making it difficult for competitors to replicate or imitate.
- Enhanced Market Position: Strong intangible assets help businesses establish a strong market position. A well-known brand, for example, can attract more customers, command higher prices, and enjoy customer loyalty, ultimately leading to increased market share.
- Increased Company Value: Intangible assets contribute significantly to a company’s overall value. When businesses can effectively leverage their intangible assets, it can result in higher profitability, investor interest, and potential for mergers and acquisitions.
- Protection and Exclusivity: Intellectual property rights provide legal protection to businesses, preventing others from using or profiting from their innovations or creative works. This exclusivity allows businesses to maintain control, capitalize on their assets, and generate revenue.
- Long-term Sustainability: Intangible assets, such as customer lists and brand equity, contribute to long-term sustainability. Building strong customer relationships and brand loyalty ensures that businesses can retain customers and maintain a steady revenue stream.
Valuation Of Intangibles
In the world of business, intangible assets play a crucial role in determining a company’s value. These assets, which lack physical form, can include intellectual property, brand reputation, customer relationships, and more. Valuing intangibles can be a complex process, but it is essential for businesses to accurately assess their worth.
Methods Of Valuation
When it comes to valuing intangible assets, businesses often utilize a variety of methods. These methods help determine the fair market value of these intangibles and provide insights for decision-making. Some common methods of valuation include:
- Income Approach: This method focuses on estimating the future benefits or cash flows that an intangible asset is expected to generate. It involves analyzing factors such as revenue streams, royalty rates, and licensing agreements.
- Market Approach: This method involves comparing the intangible asset to similar assets in the marketplace to determine its value. Market data, including recent transactions and industry benchmarks, are considered to assess the asset’s worth.
- Cost Approach: This method determines the value of an intangible asset by calculating the cost to recreate or replace it. This approach takes into account the expenses associated with research and development, production, and marketing.
Key Considerations In Valuing Intangibles
Valuing intangibles requires businesses to carefully consider certain factors that can influence their worth. These considerations can impact the outcome of the valuation process and include:
- Market Conditions: The current market conditions, industry trends, and competitive landscape can significantly affect the value of intangible assets.
- Legal and Regulatory Factors: Compliance with intellectual property laws, licensing agreements, and contractual obligations can impact the value of intangibles.
- Brand Strength: The reputation, recognition, and customer loyalty associated with a brand can heavily influence the value of intangible assets.
- Technology Advancements: Technological advancements and innovation can either enhance or diminish the value of intangibles, especially in industries driven by intellectual property.
In conclusion, the valuation of intangibles is a crucial aspect of business decision-making. By using various valuation methods and considering key factors, businesses can accurately assess the worth of their intangible assets, enabling them to make informed strategic choices.
Managing Intangibles
When it comes to running a successful business, managing intangibles is just as crucial as managing tangible assets. Identifying and assessing intangibles allows businesses to understand the value of these non-physical assets, while implementing strategies for managing intangibles ensures that they are effectively utilized to drive business growth. In this section, we will delve into the process of identifying and assessing intangibles, and explore effective strategies for managing these valuable resources.
Identifying And Assessing Intangibles
Intangible assets are valuable resources that do not have a physical form, but hold significant value for a business. Some examples of intangibles include brand reputation, intellectual property, customer loyalty, and employee expertise. Identifying and assessing these intangibles is essential to understand their impact on the business and determine their overall value.
- Start by conducting a thorough inventory of all the intangible assets your business possesses.
- Categorize them into different types such as brand, human capital, intellectual property, or customer-related intangibles.
- Assign a value or weight to each intangible asset based on its importance and potential impact on the business.
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each intangible asset, and identify any potential risks or threats.
By having a clear picture of the intangibles your business possesses and their value, you can make informed decisions about how to best manage and leverage them for business growth.
Strategies For Managing Intangibles
Once you have identified and assessed your intangibles, it’s time to develop strategies to effectively manage and utilize them. Below are some effective strategies that can help you make the most of your intangible assets:
- Develop a comprehensive intellectual property protection plan to safeguard your valuable intangible assets from infringement or theft.
- Invest in employee training and development programs to enhance their skills and expertise, as well as foster a culture of innovation and knowledge sharing.
- Build strong customer relationships and loyalty by delivering high-quality products or services and providing excellent customer service.
- Establish and maintain a strong brand reputation through strategic marketing and branding efforts.
- Regularly monitor and measure the performance of your intangible assets to identify areas for improvement or potential risks.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively manage your intangible assets, maximize their value, and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Legal Protection Of Intangibles
Legal protection of intangibles is crucial for businesses. Intangible assets, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights, are valuable assets that need to be safeguarded. Proper legal measures ensure that these assets are protected from infringement and misuse, allowing businesses to maximize their value and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
When it comes to protecting your intangible assets, it’s crucial to understand the various legal avenues available to safeguard your intellectual property and maintain a competitive edge in the business world.
Intellectual Property Rights
Intellectual property rights (IPR) grant legal protection for intangible assets. These rights allow creators and innovators to exclude others from using, copying, or profiting from their inventions, works of art, brand names, or trade secrets.
Here are some key forms of intellectual property rights:
- Patents: Patents protect new inventions and technologies, granting exclusive rights for a limited period of time.
- Trademarks: Trademarks protect unique symbols, logos, or phrases that distinguish a particular brand or product from others.
- Copyrights: Copyrights safeguard original works of authorship, such as books, music, artwork, and software.
- Trade Secrets: Trade secrets protect confidential business information, such as manufacturing processes, formulas, or customer lists, which give a competitive advantage.
Contracts And Agreements
Contracts and agreements are powerful tools to protect intangibles and establish legal boundaries. These agreements outline the rights and obligations of involved parties and can include provisions for non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), non-compete clauses, and intellectual property assignment.
These contracts should clearly define the ownership, usage rights, and restrictions related to intangible assets, limiting the risk of misuse, unauthorized disclosure, or infringement.
Summary
In conclusion, the legal protection of intangible assets is crucial for businesses to maintain their competitive position and safeguard their intellectual property. By securing intellectual property rights and implementing robust contracts and agreements, businesses can ensure their intangible assets are protected from unauthorized use or infringement, fostering innovation and driving growth.
Monetizing And Exploiting Intangibles
Intangible assets hold significant value for businesses, and leveraging these assets can be a key driver of success. Monetizing and exploiting intangibles can help companies maximize their potential and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Licensing And Franchising
Licensing and franchising are effective strategies for monetizing intangibles. Through licensing, businesses can grant permission to other entities to use their intangible assets, such as patents, trademarks, or copyrights, in exchange for royalties or fees. Franchising, on the other hand, allows businesses to expand their operations by replicating their successful intangible assets in a new market, thereby generating revenue through franchise fees and ongoing royalties.
Sale And Transfer Of Intangibles
The sale and transfer of intangibles provide opportunities for businesses to capitalize on their intangible assets. This can involve outright sales of patents, trademarks, or copyrights to other companies, or the transfer of rights to use intangible assets in specific territories or industries. Such transactions can yield significant financial returns and strategic benefits for the originating businesses.
Frequently Asked Questions On Intangible Definition Business
What Is An Example Of An Intangible?
Examples of intangibles are goodwill, brand recognition, copyrights, patents, trademarks, trade names, and customer lists. These are long-term assets used by companies for more than a year. Intangible goods include travel, insurance, consulting, and education. Intangible resources are strategic information and assets used to achieve business goals.
Intangible concepts are abstract ideas, feelings, and beliefs. Intangible assets have no physical form and can include intellectual property, relationships, and goodwill.
What Are Examples Of Intangible Goods?
Examples of intangible goods include goodwill, brand recognition, copyrights, patents, trademarks, trade names, and customer lists. These assets have value but do not have a physical form.
What Does Intangible Resources Mean In Business?
Intangible resources in business refer to non-physical assets like knowledge, information, and intellectual property that a company can utilize to achieve its goals. Examples include trademarks, patents, goodwill, and customer lists. These assets have long-term value and are not tangible.
What Is The Definition Of Intangible Concept?
An intangible concept is an abstract idea, feeling, or value that lacks physical form. Examples include relationships, beliefs, and universal concepts.
Conclusion
In business, intangible assets hold significant value. From brand recognition and trademarks to patents and copyrights, these assets contribute to long-term success. Intangible resources, such as strategic information and knowledge assets, offer organizations the flexibility and advantage they need to achieve their goals.
Unlike tangible assets, intangibles cannot be touched or seen, yet their impact is undeniable. Understanding the importance of intangible assets and leveraging them wisely can greatly benefit businesses in the ever-evolving digital landscape. So, make sure to recognize and nurture these intangible assets to stay ahead in the competitive business world.

Park Yeh stands as a distinguished expert at the crossroads of finance, investment, and risk management. With a comprehensive background in the share market, loan management, and risk assessment, she has become a trusted advisor in the intricate world of financial strategy. Park Yeh possesses a keen understanding of the share market, where she navigates market trends and provides insights to guide investment decisions. Simultaneously, her proficiency in loan management and risk assessment showcases a unique ability to balance opportunities and potential pitfalls in financial transactions. Park Yeh’s expertise extends further into the realm of gold nugget investments, where she demonstrates a strategic approach to precious metal markets. As a multifaceted professional, Park Yeh continues to contribute to the financial landscape, offering valuable guidance to individuals and organizations seeking informed and diversified investment strategies. Her insights into share markets, loan management, risk assessment, and gold investments make her a well-rounded and respected figure in the world of finance.